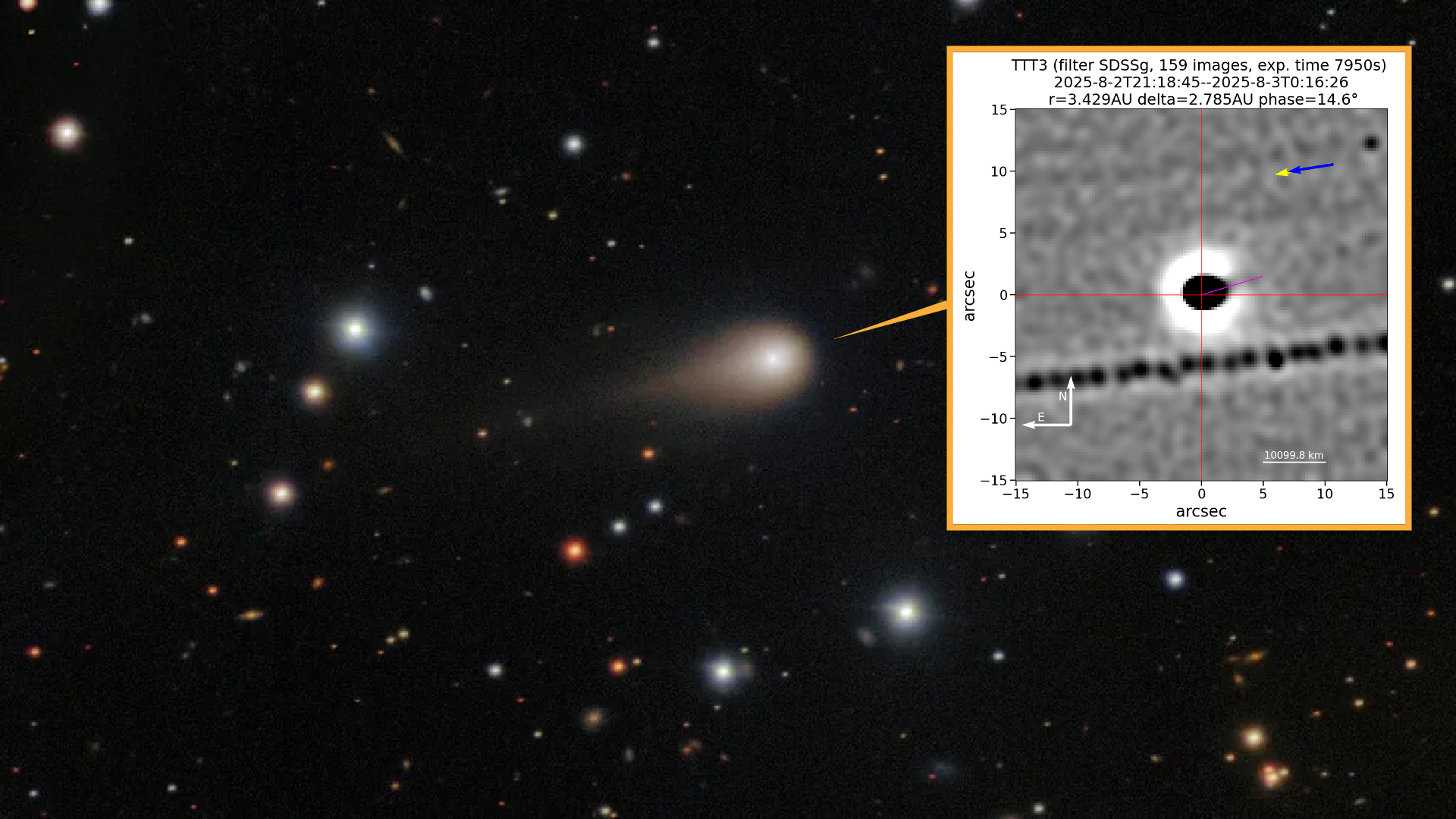
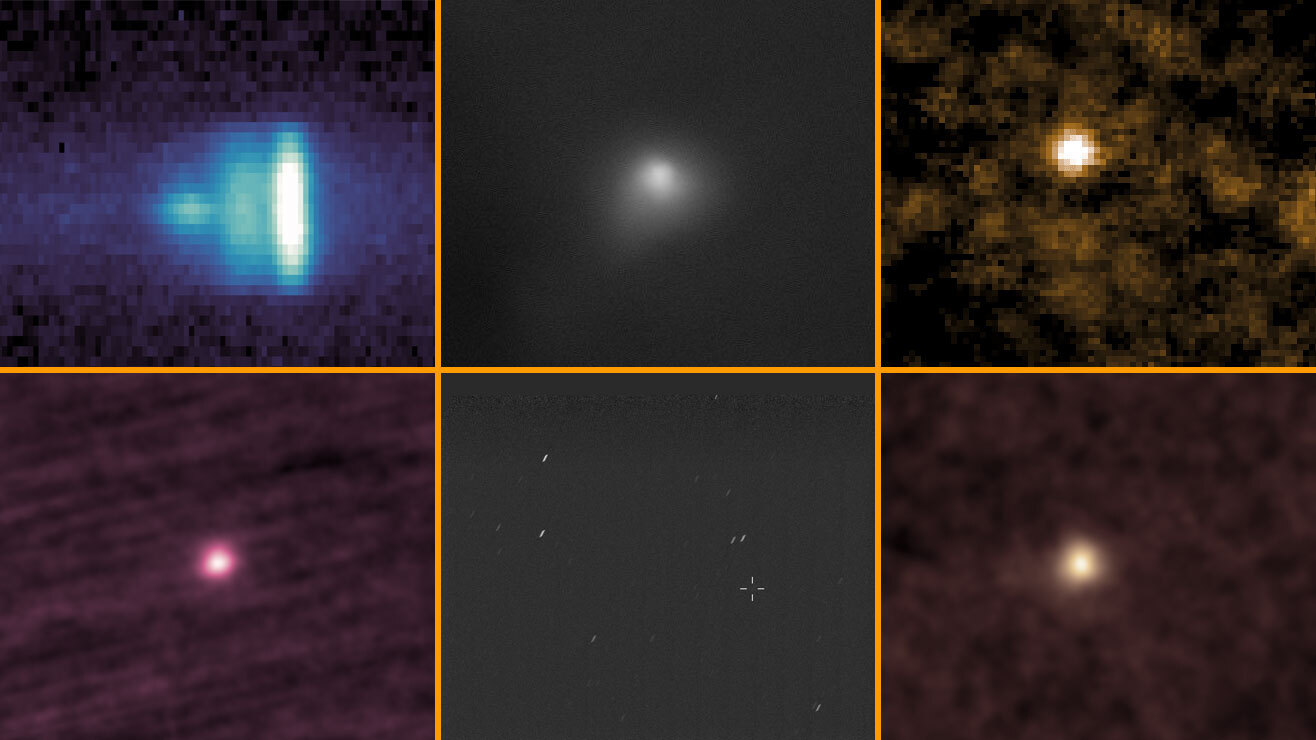
We've watched it speed through the solar system using the most powerful telescopes in human history. We've studied its light with probes whipping around the sun and robots marooned on Mars. Countless eyes watched it make its closest approach to Earth on Dec. 19 — and yet, for all of this, the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS remains little more than a blur of gas, shrouded in mystery.
Since its discovery in early July, 3I/ATLAS has been studied more enthusiastically than practically any other celestial object in recent memory. Still, for all its fame, much remains unknown about it. The comet’s origins, from somewhere far across our galaxy, may never be known. Its true age, size, composition, and shape are also poorly constrained.
But how can we learn more about this alien interloper — or indeed, the next one — when we’re already studying it with everything we’ve got?
Alien interlopers
On July 1, astronomers at the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) revealed they had spotted a mysterious object traveling toward us from beyond Jupiter, at more than 130,000 mph (210,000 km/h). ATLAS, which automatically scans the skies using telescopes in Hawaii, Chile and South Africa, was hunting for potential threats to Earth. It found something else entirely.
Less than 24 hours later, NASA confirmed that the speeding blur of light was an interstellar object — an alien asteroid or comet that originated outside the solar system — and named it 3I/ATLAS. It was only the third-ever detection of an interstellar object in our solar system, after the anomalous space rock ‘Oumuamua in 2017 and Comet 2I/Borisov in 2019.
Despite the rapid spread of unfounded theories that the object could be an alien probe, early observations confirmed that 3I/ATLAS is a comet — potentially the oldest of its kind ever seen — that likely originated from the Milky Way's “frontier” region.
Interstellar visitors like this are exciting to astronomers because they are one of the few opportunities we have to explore neighboring star systems, which would take generations and the invention of sci-fi technology to reach aboard a spacecraft.
“ISOs are relics from planetary formation, so studying these objects and comparing them to what we have closer to us [could] lead to an interesting view of how other planetary systems in the galaxy formed,” Pedro Bernardinelli, a planetary scientist at the University of Washington's DiRAC Institute, told Live Science in an email.

But our Earth-based observatories, and even orbiting spacecraft such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), can only tell us very rough information like general size, shape and composition. To really reveal ISO secrets, we will need to get much, much closer — possibly even close enough to grab a fragment.
Doing so won't be easy, but given the valuable insights it could reveal about the star systems beyond our own, it would be well worth the effort, experts say.
“Each one of these ISOs is a little piece of low-hanging fruit from a tree that can tell us a great deal about the trees growing in some other neighborhood,” Wesley Fraser, an astronomer with the National Research Council Canada, previously told Live Science.
Giving chase
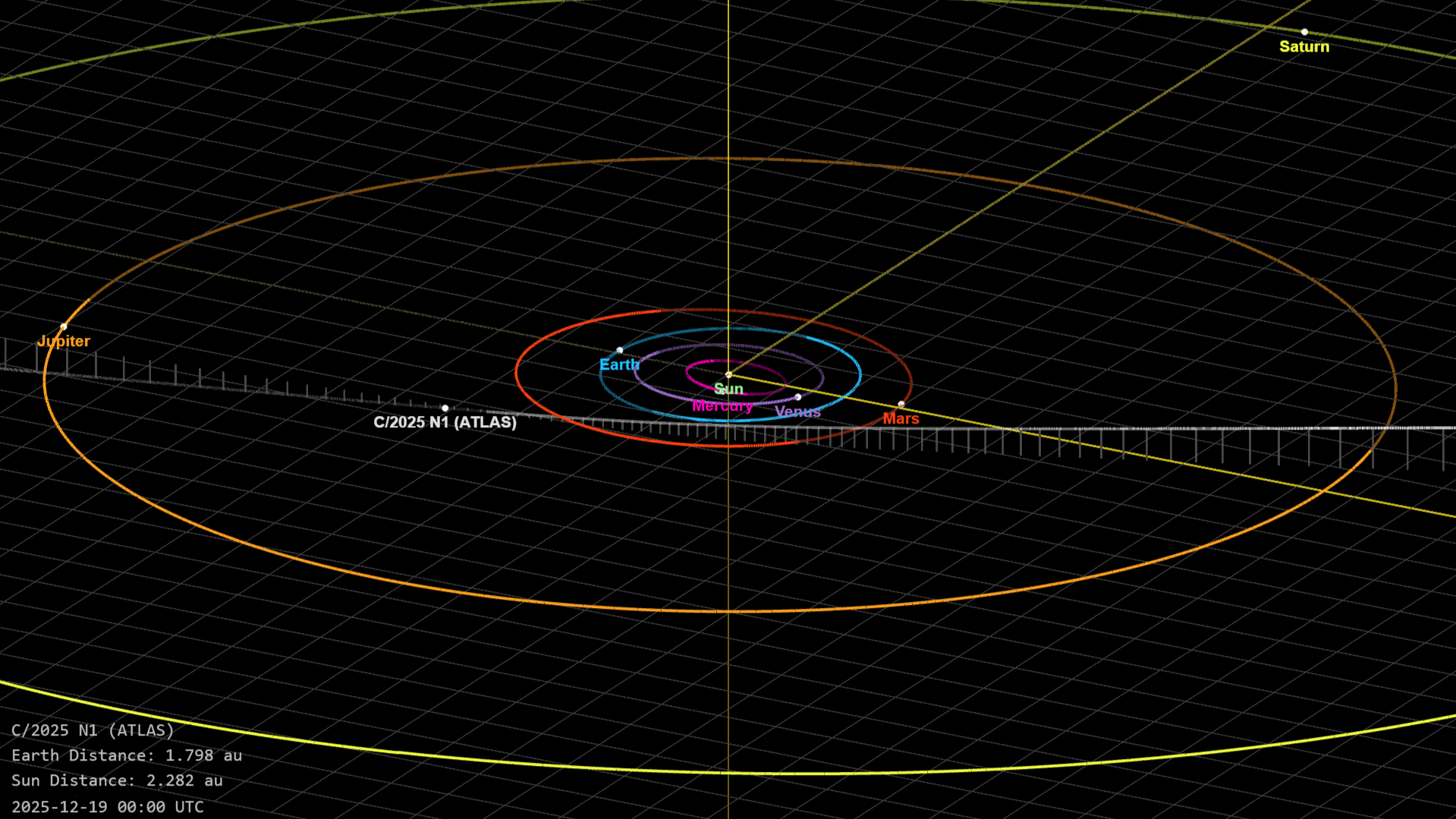
But the time to catch this speeding comet is fast approaching. 3I/ATLAS is now reaching its closest point to Earth, around 168 million miles (270 million km) miles away. From there it will move quickly away from us and will likely be beyond Neptune within another year.
Because it is now too late to intercept 3I/ATLAS within the inner solar system, most researchers agree that there is now only one viable option to study this object: to chase it down as it leaves the solar system.
This would require the spacecraft to carry out what researchers call “Oberth maneuvers,” where a probe is gravitationally slingshotted around massive objects, such as the sun, to pick up enough speed to allow it to catch up to and intercept an ISO at a specific point along its predicted trajectory.
This idea was first proposed in 2022 to catch up with the first known interstellar object, ‘Oumuamua. The plan, dubbed Project Lyra, was to launch a probe in 2028 that would intercept and investigate that object, after completing an Oberth maneuver around Jupiter.
But this chaser method has a huge limitation: Scientists would need to wait decades for data to come back. For example, if Project Lyra launched a spacecraft in 2030, it would not intercept ‘Oumuamua until 2052 at the earliest, Adam Hibberd, a researcher with the U.K.-based nonprofit Initiative for Interstellar Studies (I4IS) who worked on Project Lyra, told Live Science.
So far, Project Lyra has not moved past the planning stage — making a 2028 launch highly unlikely — but the project could still reach ‘Oumuamua if launched in 2030 or 2033, Hibberd said. This means we would likely still have plenty of time to chase down 3I/ATLAS, if we want to.
Future propulsion methods, such as a solar sail, could drastically cut the travel time of missions like this from decades down to just a few years, he added. But these technologies are decades away from becoming a reality themselves.
Playing “hide-and-seek”
But given that 3I/ATLAS will be very hard to chase down, some astronomers argue that we shouldn't bother hunting it. Rather we should prepare to intercept the next interesting ISO.
By launching an interceptor spacecraft and parking it in a gravitationally stable position around Earth, known as a Lagrange point, we could, in theory, be ready to quickly intercept a passing object, they argue.
This idea, also first proposed in 2022, has been dubbed the “hide-and-seek” approach. However, unlike Project Lyra, it is much closer to becoming a reality.
The European Space Agency (ESA) is preparing the Comet Interceptor mission, which is currently scheduled to launch in 2029, on board the same rocket as ESA's Ariel space telescope, said Colin Snodgrass, an astronomer at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland who specializes in comets and was the deputy project investigator on the proposal for this mission.

The Comet Interceptor probe isn't specifically aimed at interstellar visitors. Instead, it's designed to hunt nonperiodic comets like Comet Lemmon, which has been visible in the night sky, alongside 3I/ATLAS, in recent months. These comets drift toward the sun every few hundred or thousand years and have poorly defined orbital pathways around the sun.
When ESA researchers spot a comet they can reach, they will “fire the rockets, get to the right place in space to cross the path of the comet and have this fast flyby encounter, where we go shooting past the comet, getting as much data as we can,” Snodgrass told Live Science.
And while the mission is not designed to study interstellar objects, the project will be perfectly placed to intercept them.
“The whole science team is very much in agreement that if an interstellar object was to pop up, we wouldn't let that opportunity go by,” Snodgrass said.
The main advantage of the hide-and-seek approach is that we wouldn't have to wait decades for a probe to catch up to its target. Additionally, we'd be reaching it at the best time to study it. That's because interstellar comets, like 3I/ATLAS, soak up more solar radiation when in the inner solar system — which, in turn, means they give off more light, gas and dust, giving us a better chance to learn about their composition.
However, a hide-and-seek mission might not be able to catch all the objects we care about. For example, ESA's Comet Interceptor probe would have been unlikely to reach 3I/ATLAS, had it been in orbit when the ISO was first discovered, because the comet was too far away from us, a recent study from Snodgrass and others found.
Collision course
A major limitation of both the chaser and hide-and-seek missions is that ISOs travel too fast for their respective spacecraft to travel alongside, or rendezvous with, these objects.
This makes it “almost impossible” for the probes to directly obtain samples from the objects' surfaces as NASA did during its OSIRIS-REx mission, which successfully landed a probe on the asteroid Bennu in 2020 and collected samples that were later returned to Earth, Hibberd said. Due to fuel limitations, it is also unlikely that these samples could be easily returned to Earth, especially during a chaser mission, he added.
However, there is a third option that could yield valuable interstellar samples: the “impactor” method.
Similar to NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, which successfully deflected the asteroid Dimorphos after smashing into the space rock in 2022, an interceptor probe could also be sent to crash into an ISO, Hibberd suggested. While this probe would be destroyed, a second spacecraft could be deployed to analyze the debris field and potentially even collect leftover fragments of the alien object, he added.
But an impactor mission would need to overcome serious technical challenges. First, ISOs travel much faster than solar system objects, like Dimorphos, meaning it's more difficult to smash them apart. Second, this method would likely work only on an asteroid, not on comets, which have hard, icy shells. And third, a collision could accidentally send chunks of debris on a collision course with Earth, like DART did. As a result, most of the experts who talked to Live Science, including Hibberd, agreed that it is probably too risky to attempt an impactor mission until more research has been done on the subject.
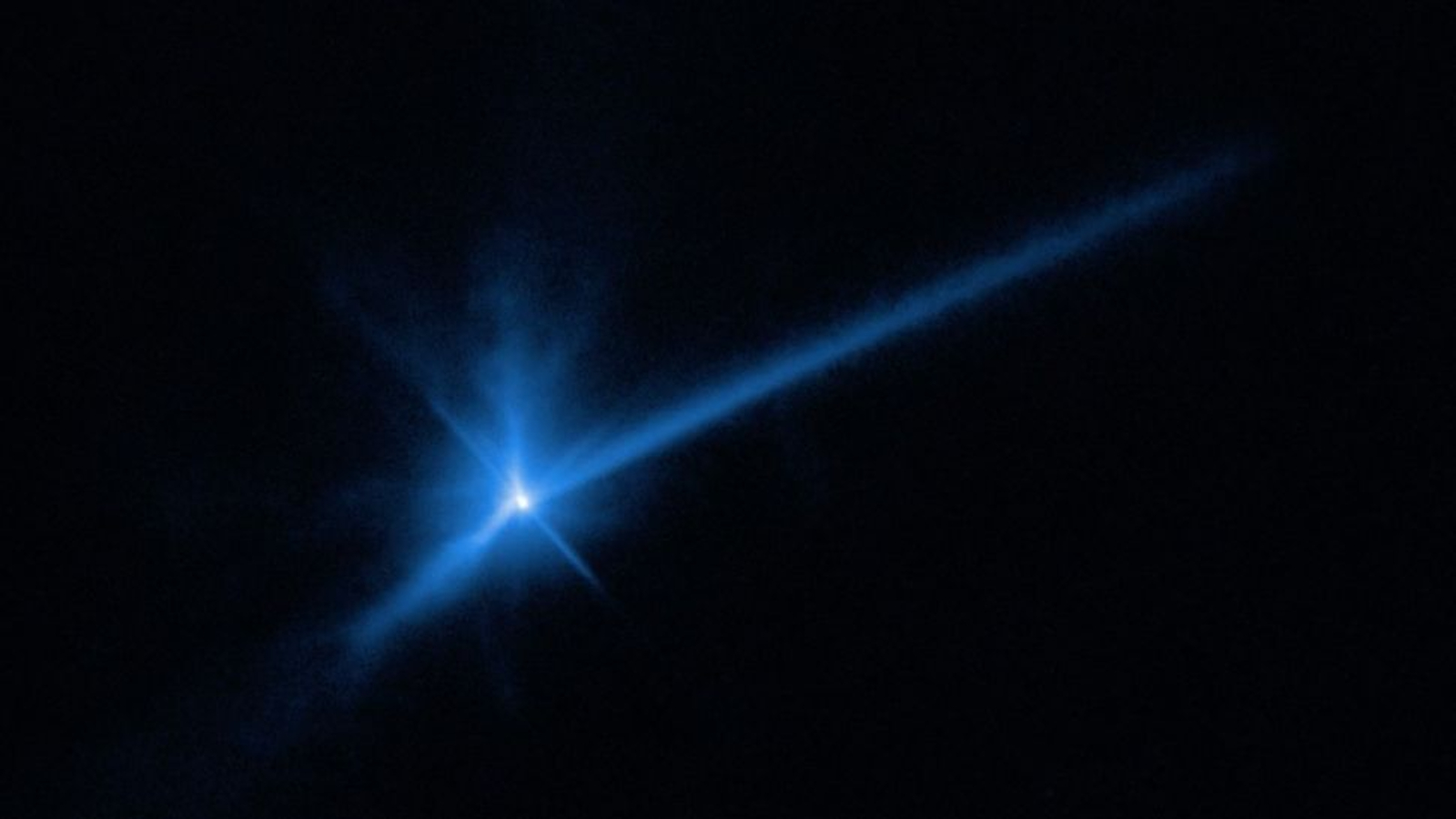

The perfect mission
If money were no object, we could pursue all of these options. But if an agency like NASA has the budget for only one such mission, which one should be selected?
A chaser mission would allow astronomers to target a specific object they know they want to study, while a hide-and-seek mission would be limited to objects that happened to pass nearby. On the other hand, the hide-and-seek mission could reliably predict objects' locations in the inner solar system, whereas the chaser method would target objects in the dark, more chaotic outer solar system, where it would be harder to find and photograph them, Snodgrass said.
Another issue is that signals from a more distant chaser mission would take longer to send and receive, so mission operators would be unable to monitor and adjust an ISO flyby in real time or fix technical difficulties easily — a difficulty NASA faces with its distant Voyager probes, Snodgrass said.
There is also the matter of money. Project Lyra would likely cost the same as NASA's New Horizons mission, which flew by Pluto in 2015 and cost at least $700 million, Hibberd said. Meanwhile, ESA's Comet Interceptor mission has a budget of around $150 million, Snodgrass said.
As a result, most researchers who spoke to Live Science agreed that a hide-and-seek interceptor would likely be the best way of studying an ISO up close.
But if this is the method we end up using, how should we design the resulting spacecraft to maximize its chances of collecting useful data?
While ESA's Comet Interceptor is relatively inexpensive, a dedicated ISO interceptor mission — with a bigger budget — would allow us to launch a faster probe that could carry more fuel and thus travel farther. However, the craft doesn't need to be fancy.
A “fairly stripped-back” probe with a decent camera and a few spectrographs, capable of analyzing the light given off by the different gases, would be more than enough to collect sufficient data from any flyby, Snodgrass said.
If the probe were intercepting a comet, and not an asteroid, it could also be fitted with a device to catch specks of dust from the comet's coma or tail during a superclose approach, just as NASA's Stardust probe did with “Comet Wild 2” in 2004.
Assuming that the interceptor hasn't depleted its fuel reserves and can be returned to Earth, this may be the only reliable way of actually getting our hands on interstellar samples, Snodgrass said.
To intercept or not to intercept
Once the “perfect” interceptor is in position around Earth, researchers will have to choose which ISO to go after. And because any spacecraft is unlikely to be reusable, it may get only one shot at picking the right target.
We may soon be spoiled for choice. ISOs may be far more common than we realize. “There are likely thousands of other ISOs in the solar system right now,” Fraser said. “We just can't see them because they are too faint, too far and too fast.”

But thanks to the newly operational Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile, which is designed to spot more small and dim objects in the outer solar system, we are likely to find many more ISOs in the coming decades and, more importantly, spot them much earlier on their journey toward us, which would give us a better chance of studying them.
The first thing to consider is whether to go after an asteroid or a comet. Because comets become more active near the sun and present the most likely route for collecting interstellar samples, they would likely take priority, Snodgrass said.
The next consideration would be the target's distance from Earth. As we have already seen, ESA's Comet Interceptor may have struggled to reach 3I/ATLAS on its journey through the inner solar system. Therefore, it might pay to wait for an ISO that is on a favorable trajectory relative to Earth.







