How would you answer the question: “How many people did you live on this planet when?” If you introduce this to Google or chat -Bot of artificial intelligence, you will receive the answer quite quickly – usually 117 billion. This number, at least, in my opinion, seems too small. In the end, the population of the world currently It is estimated at 8.2 billion people. This means that we make up about 7 percent of all people when they are born.
The figure of 117 billion includes every person who has ever seen light, including those who died young. However, the expectation of life has increased all over the world. As a result, there are other strange issues of the population. For example, the article of 2014 in A Economist She stated that half of all people who were once at the age of 65 or older are alive TodayCan this really be true? And how do you even calculate something like that?
Demographers have asked such questions for decades. One of the biggest problems that they face is the data: you need to know how many people lived at different times, as well as the average life expectancy or birth rate. Such numbers are available today (although notes are not always reliable), but less for centuries. Statistical analysis and census were not carried out everywhere in all societies. Therefore, demographers must significantly rely on assessments.
On the support of scientific journalism
If you like this article, consider the opportunity to support our journalism awards SubscriptionWhen buying a subscription, you help to ensure the future of effective stories about discoveries and ideas that form our world today.
And then there are several fundamental issues that need to be considered. What exactly is meant by “man”? We mean all members of the clan Homo Who passed our planet or just Homo sapiens in particular? Given the problems, it is surprising that when assessing all the people who once lived, we usually have only one number, 117 billion, and not a range with a low and high rating. I argue that this is completely appropriate from a scientific point of view and signals that the result is an approximation. The order of magnitude may seem plausible, but you cannot answer the question for sure.
Modeling population growth
In order to realistically evaluate an assessment of 117 billion people, you first need data. From the 20th century to the present, you can find many digits of the population thanks to the regular census conducted in many countries since the 1850s.
Looking further in history, the number of living people can be approximately assessed depending on the size of cities and population density. Over the earlier times, archaeological remains offer tips.
Nevertheless, Some sources Place the population of the world per year for 1 year in 170 million people, while others – 300 million, almost twice as much. There is also a question about how far we should even watch. There are estimates in which Demographers return to 4.5 million years Consider all members of the genus HomoField Others, however, are focused on Homo sapiens And look back from 50,000 to 200,000 years.
Over the years, not only the number of living people, but also the corresponding level of population growth has changed significantly. The population of the world previously increased very slowly, but, in the visible one, grew faster in the last centuries. This is due to the fact that the birth rate has decreased, while the mortality rate has decreased even more – a combination that can be difficult to simulate.
However, it can be assumed that the growth rate is constant for small time intervals. Demographers use this assumption to assess the number of living people at a given time interval. You must divide the period under consideration into different sections; For example, you can start 50,000 years before our era and end in 2025. The more units you make, the more accurate the result.
If we now assume that the birth rate clay and mortality rate With are constant within the framework of this time scale, and then the population Not Changes in accordance with the following differential equation:
Given that clay And With It is assumed that it is constant within the interval, the size of the population in this area can be simulated using an exponential function: Not(T) = Not0EnCtWhere are the parameters K. (Pure growth rate) and Not0 (Population size, when time T = 0) are determined by data points.
To determine how many people lived when they lived, you must add the number of living people at every moment in time TThis can be done by calculating the integral of a piece-determined function. T In the corresponding section:

This approach conveys the actual answer, although. Think about it like this: if you read this article, then you are currently alive; However, you were most likely already alive 10 years ago, and also contributed to the world population. Therefore, the integrated result should be divided into the corresponding life expectancy of people who lived during the period under consideration. In the end, you can add results for all time periods and –This!– The result should correspond to the total number of people who once lived.
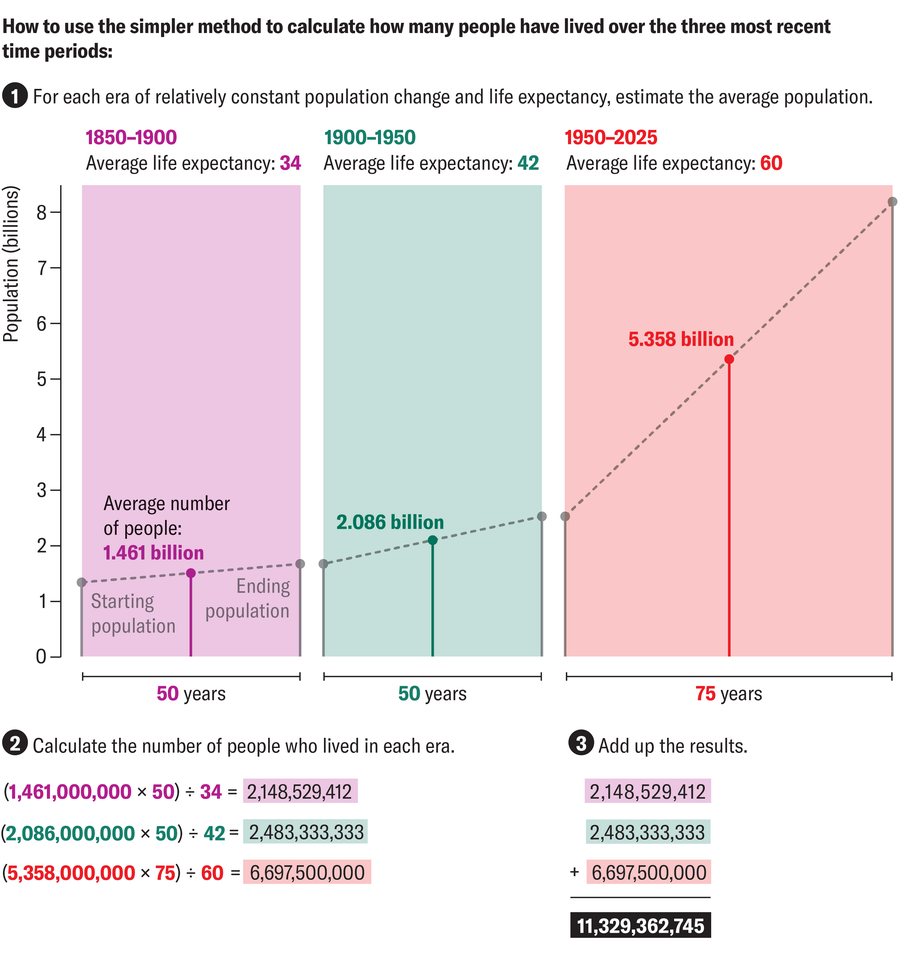
Technically, there is a simpler approach, like a German mathematics teacher Bruno's neck demonstrated With a school project. He set his students the same task: they had to assess the number of all people who once lived. But these students did not yet know how to calculate the integral of the exponential function.
One group of students decided to simply calculate the average value for certain time intervals. For example, if in 1945 there were about 1.6 billion people in 1945, students suggested that on average 2.05 billion people lived during these 45 years. Then they multiplied these average values by the corresponding period of time (in this case 45 years) and divided them by the average expected life expectancy that people had at that time (on average in life in 1900 and 1945). This method gave the group an approximate assessment of the entire world population without the need to resort to complex calculation methods, such as integrals.
Two methods with surprisingly similar results
To compare these methods, you can calculate the number of the population using an example. I decided to use the data which were previously used by the demograph in Karl Haube in an article by the Bureau of the population, published in 2011.He suggested that humanity occurred 50,000 years ago with two people. He also appreciated the expected life expectancy for each temporary interval.
I added a final data point with the alleged population and life expectancy in 2025.
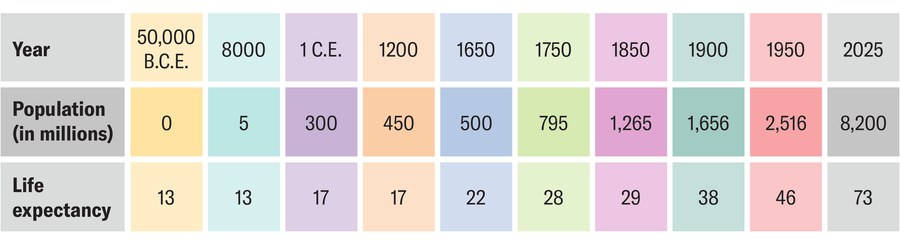
In total, 10 points are available in this example, that nine nine sections. Inside this, you can determine the right exponential functions for modeling the corresponding growth. By dividing them into the average life expectancy during this period, you can get the number of people at that time.
This leads to the conclusion that a little more than 93 billion people were born when they were born. The figure of 117 billion is based on a recent assessment of HAUB and demographer Toshiko Kaned What appeared in 2022 with updated population dataThe field (researchers, among other things, suggested that the human race occurred 200,000 years ago.)
If you use a simpler calculation method used by the neck students, to the data from the above table, the final result is more than 140 billion – much more than the result obtained by another method. This difference may seem large, but in fact it is impressive that it ultimately becomes the same order.
What about people aged 65 and older?
Two submitted approaches allow us to evaluate how many people were born when they were born. But what about the statement of the journalist Fred Pierce In his book 2010 The upcoming accident The fact that of all people who have reached 65 years old, half of them are alive today? In 2017, a team of demographers led by Miguel Sanchez-Romero from the Center for Demography and Global Capital Wittgenstein I studied this statement After he surfaced in 2014 Economist articleThe researchers have developed two different demographic models for research: one, in which the population growth was constant, and the second, in which they considered the hyperbolic growth of the population.
They also used various data sets for their modeling to ensure realistic errors. Their conclusion: Fred Pierce was incorrect. “Indeed, such a number would never be achievable, theoretically (in a stable population), nor empirically in accordance with the existing data,” they wrote in their article.
According to their calculations, the share of people who once reached 65 years and older, who are alive today, is from 5.5 to 9.5 percent. This means that even in the most extreme case, a little less than 10 percent of all people who were at the age of 65 and older are alive today. Even if this significantly softens the initial statement of the pier, I still find the result quite amazing. Imagine that there was a kind of lottery, which decided at what moment of human history you would be alive based on your life. If you have reached the age of 65, you will be likely that you have about one out of 10 people, even if you take into account the last 200,000 years.
This article initially appeared in The spectrum of science And he was reproduced with permission.








