For many years, needing reading glasses to correct farsightedness seemed like an inevitable part of aging. Visual accessories may officially be a thing of the past this year. VIZZ eye drops from LENZ Therapeutics offer a new treatment for age-related farsightedness. The newly approved drops are effective enough to improve vision by three or more lines on an eye chart in just 30 minutes.
This is why such a widespread impact Popular Science chose the drops as the winner in the “Health 2025” category. This year's list also includes groundbreaking improvements in pediatric heart transplants, a potential cure for a deadly blood cancer and a minimally invasive treatment for prostate cancer.
(Editor's note: This is an excerpt from Popular Science's 38th Annual “Best of New” Awards. Be sure to read complete list of the 50 greatest innovations of 2025.)
Winner of the Grand Prix in the field of healthcare
VIZZ from LENZ Therapeutics: eye drops correct age-related farsightedness for up to 10 hours at a time
Find out more
Presbyopia, an age-related farsightedness that causes people to need reading glasses, affects 128 million people in the United States and about 2 billion people worldwide. This is one of the few conditions that is virtually guaranteed if you live long enough. Now eye drops called VICEdeveloped by LENZ Therapeutics, offers patients with presbyopia vision correction for 10 hours at a time.
Aceclidine ophthalmic solution received FDA approval for the treatment of presbyopia in July. Aceclidine, previously known in Europe as a common glaucoma treatment, acts on the iris to shrink the pupil. The smaller the pupil, the greater the depth of field. In trials involving 1,059 participants aged 45 to 75, VIZZ improved near vision by three or more lines on eye charts within 30 minutes. The researchers reported that participants were able to read on phones and tablets without reading glasses and had no loss of distance vision. The result lasted up to 10 hours.
Previously, other presbyopia drops that targeted a different part of the eye—the ciliary muscle, located behind the iris—caused eyebrow pain in some users. For VIZZ users, the most common adverse reactions are eye irritation, blurred vision, redness and headache. The company also recommends consulting with an eye care professional before starting them, since miotics like VIZZ may increase the risk of retinal tears.
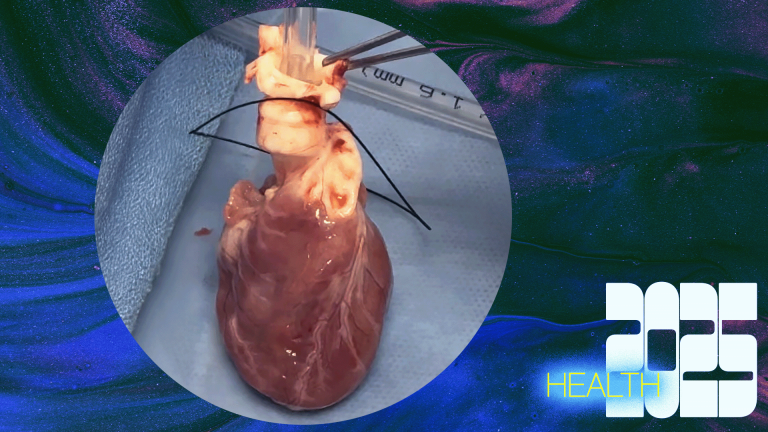
Resuscitation of a pediatric heart from donor material after cardiovascular death on the table, Duke University Medical Center: expanding the donor pool for children in need of a heart
Find out more
Infants are much more likely than adults to die while waiting for a heart transplant. In 2022, a study of the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients found that more than 1,100 children were on the waiting listand hundreds more are added every year. Due to the small number of donors and the lack of devices suitable for pediatric transplantation, up to 20% of these children will die while waiting. The most common type of heart donation is donation after brain death (DBD). However, one way to expand the donor pool would be to include heart donation after cardiovascular death (DCD), or after the donor's heart stops beating. A well-known technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP) is resuscitating DCD's heart so it can be donated. However, the NRP raised ethical issues related to determining death and restoring blood flow to a dead body. As a result, this method is banned in many institutions, and viable donor hearts, including children's, often go unused.
In an attempt to circumvent the heated debate over NRP and increase the number of donors for babies in need, a team at Duke University Medical Center developed resuscitation technique on the tablea system with a special circuit that resuscitates the DCD heart outside the body directly on the operating table. Because this all happens outside the body, the new technique bypasses many of the limitations of NRP. Using a new technique, the team successfully transplanted a heart from a one-month-old donor to a three-month-old recipient. The child recipient has been healthy and healthy ever since, according to Dr. Joe Turek, a pediatric heart surgeon at Duke University.
The Duke team is now introducing the technique to colleagues across the country. Widespread implementation of this method could increase the pool of donors for pediatric heart transplantation by up to 20% and save countless children's lives. According to Duke's team, the technique could be applied to adult heart transplants, offering a less expensive way to deliver donor hearts to patients in need.
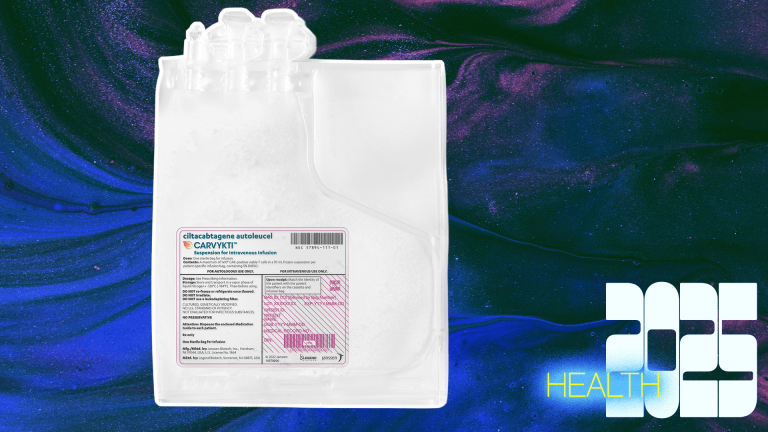
Carvykti from Legend Biotech and Johnson & Johnson: a possible cure for deadly blood cancer
Find out more
Multiple myeloma has long been considered incurable. Deadly blood cancer is a disease that 36,000 Every year Americans develop, they eat away at their bones, creating holes that weaken the skeleton. At an important milestone study Carvykti, a CAR-T immunotherapy published this year, has shown long-term results. remission and survival for patients with multiple myeloma. Of the 97 patients treated, cancer disappeared in one third. This is an amazing result for people who have faced death after trying everything before treatment. Because some patients are now completely disease-free five or even seven years after treatment, researchers are urging colleagues to consider using the four-letter word forbidden in cancer medicine: treatment.
Developed in China by Legend Biotech, which then merged with Johnson & Johnson, Carvykti works by extracting a patient's own white blood cells, retraining them to fight cancer, and then reinfusing them back into the body. Unsurprisingly, this can be a physically grueling process.
FDA approved therapy in 2022and now it's causing a stir as follow-up studies reveal its startling long-term effects. The researchers say the results would likely be even better if Karvykti was used as an earlier line of treatment, rather than just as a last resort.
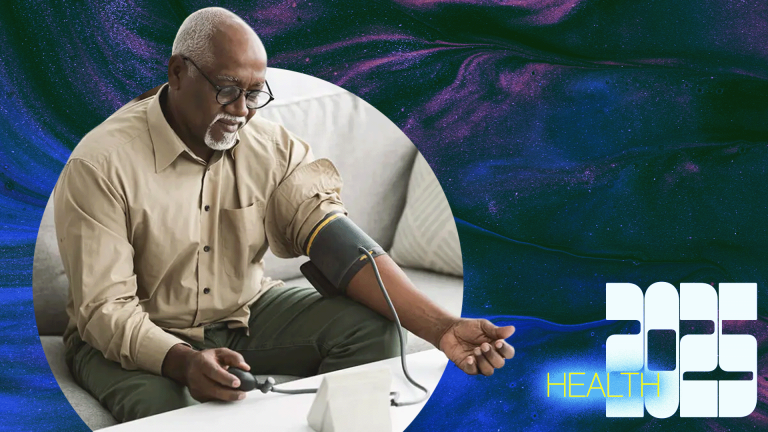
UC Davis Health's Remote Patient Blood Pressure Monitoring Program: A personalized, widely available program for treating hypertension.
Find out more
Hypertension is a chronic disease that affects almost half of Americans According to the American Heart Association, over 20 years of age. High blood pressure can put a person at risk for cardiovascular disease, heart attack and stroke. Taking control of high blood pressure can not only prolong a person's life, but also make everyday activities easier and more enjoyable. UC Davis has recently become a pioneer home monitoring program using home technology to help patients with hypertension lower their blood pressure.
The remote blood pressure monitoring program lasts for six months, but patients can extend their participation in the program for up to a year. The program includes education, medications, and blood pressure cuffs for home monitoring. Each patient receives orientation, group sessions, and personalized education on the best practices for their health, all while working remotely with a full medical team. In total, more than 150 patients are either currently participating in the program or have completed it.
Now, more than a year later, the University of California, Davis is declaring a triumph, citing an average drop in people's blood pressure of 150/80 mmHg. Art. up to 125/74 mm Hg. Art. in just a few months, which significantly reduces the risk of heart disease in patients. And participants maintain their progress even after the program ends.
UC Davis Health currently has several remote patient monitoring programs and wants to use new technologies to make care more accessible. For many reasons, such as distance, age, mobility or pregnancy, the patient will not be able to easily see the doctor as often as he needs. The UC Davis model can be useful for both rural and urban health centers. Program leaders say they are working to not only continue the program, but also expand it in the coming years.
NanoKnife from AngioDynamics: minimally invasive intervention for prostate cancer
Find out more
Every eighth man will diagnosed According to the American Cancer Society, they suffered from prostate cancer during their lifetime. Treatment may include surgery or radiation therapy, but these interventions can damage the nerves surrounding the tumor, leading to complications such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence.
Developed by AngioDynamics and FDA approved December 2024. NanoKnife sends localized electrical impulses directly to cancerous tissue with precision that avoids damage to adjacent tissue. Just as some breast cancer patients are given the option of a more targeted lumpectomy rather than treating the entire breast, eligible prostate cancer patients now have a more targeted, radiation-free alternative that does not require treatment of the entire breast.
The NanoKnife system offers men with prostate cancer that has not yet spread a minimally invasive solution with limited quality of life side effects before doctors turn to other, more aggressive treatments. It is now used in hospitals across the country.